数据库和 Doctrine ORM
视频教程
您喜欢视频教程吗?查看 Doctrine 视频教程系列。
感谢 Doctrine,Symfony 提供了在您的应用程序中使用数据库所需的所有工具,Doctrine 是用于操作数据库的最佳 PHP 库集。这些工具支持关系数据库(如 MySQL 和 PostgreSQL)以及 NoSQL 数据库(如 MongoDB)。
数据库是一个广泛的主题,因此文档分为三篇文章:
- 本文介绍了在 Symfony 应用程序中使用关系数据库的推荐方法;
- 如果您需要低级别访问以执行原始 SQL 查询到关系数据库(类似于 PHP 的 PDO),请阅读另一篇文章;
- 如果您正在使用 MongoDB 数据库,请阅读 DoctrineMongoDBBundle 文档。
安装 Doctrine
首先,通过 orm Symfony pack 和 MakerBundle 安装 Doctrine 支持,MakerBundle 将帮助生成一些代码:
1 2
$ composer require symfony/orm-pack
$ composer require --dev symfony/maker-bundle配置数据库
数据库连接信息存储为名为 DATABASE_URL 的环境变量。对于开发环境,您可以在 .env 文件中找到并自定义它:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
# .env (or override DATABASE_URL in .env.local to avoid committing your changes)
# customize this line!
DATABASE_URL="mysql://db_user:db_password@127.0.0.1:3306/db_name?serverVersion=8.0.37"
# to use mariadb:
# Before doctrine/dbal < 3.7
# DATABASE_URL="mysql://db_user:db_password@127.0.0.1:3306/db_name?serverVersion=mariadb-10.5.8"
# Since doctrine/dbal 3.7
# DATABASE_URL="mysql://db_user:db_password@127.0.0.1:3306/db_name?serverVersion=10.5.8-MariaDB"
# to use sqlite:
# DATABASE_URL="sqlite:///%kernel.project_dir%/var/app.db"
# to use postgresql:
# DATABASE_URL="postgresql://db_user:db_password@127.0.0.1:5432/db_name?serverVersion=12.19 (Debian 12.19-1.pgdg120+1)&charset=utf8"
# to use oracle:
# DATABASE_URL="oci8://db_user:db_password@127.0.0.1:1521/db_name"警告
如果用户名、密码、主机名或数据库名称包含 URI 中被视为特殊的字符(例如 : / ? # [ ] @ ! $ & ' ( ) * + , ; =),您必须对其进行编码。有关保留字符的完整列表,请参阅 RFC 3986。您可以使用 urlencode 函数对其进行编码,或者使用 urlencode 环境变量处理器。在这种情况下,您需要删除 config/packages/doctrine.yaml 中 resolve: 前缀,以避免错误: url: '%env(DATABASE_URL)%'
现在您的连接参数已设置好,Doctrine 可以为您创建 db_name 数据库:
1
$ php bin/console doctrine:database:createconfig/packages/doctrine.yaml 中还有更多选项可以配置,包括您的 server_version(例如,如果您使用 MySQL 8.0.37,则为 8.0.37),这可能会影响 Doctrine 的功能。
提示
还有许多其他 Doctrine 命令。运行 php bin/console list doctrine 查看完整列表。
创建实体类
假设您正在构建一个需要显示产品的应用程序。甚至在考虑 Doctrine 或数据库之前,您就已经知道您需要一个 Product 对象来表示这些产品。
您可以使用 make:entity 命令来创建此类以及您需要的任何字段。该命令将询问您一些问题 - 像下面这样做回答它们:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
$ php bin/console make:entity
Class name of the entity to create or update:
> Product
New property name (press <return> to stop adding fields):
> name
Field type (enter ? to see all types) [string]:
> string
Field length [255]:
> 255
Can this field be null in the database (nullable) (yes/no) [no]:
> no
New property name (press <return> to stop adding fields):
> price
Field type (enter ? to see all types) [string]:
> integer
Can this field be null in the database (nullable) (yes/no) [no]:
> no
New property name (press <return> to stop adding fields):
>
(press enter again to finish)哇!您现在有了一个新的 src/Entity/Product.php 文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
// src/Entity/Product.php
namespace App\Entity;
use App\Repository\ProductRepository;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
#[ORM\Entity(repositoryClass: ProductRepository::class)]
class Product
{
#[ORM\Id]
#[ORM\GeneratedValue]
#[ORM\Column]
private ?int $id = null;
#[ORM\Column(length: 255)]
private ?string $name = null;
#[ORM\Column]
private ?int $price = null;
public function getId(): ?int
{
return $this->id;
}
// ... getter and setter methods
}提示
从 MakerBundle: v1.57.0 开始 - 您可以传递 --with-uuid 或 --with-ulid 给 make:entity。利用 Symfony 的 Uid 组件,这将生成一个实体,其 id 类型为 Uuid 或 Ulid,而不是 int。
注意
从 v1.44.0 开始 - MakerBundle: 仅支持使用 PHP 属性的实体。
注意
困惑为什么价格是整数?别担心:这只是一个例子。但是,将价格存储为整数(例如 100 = 1 美元)可以避免舍入问题。
警告
当在 MySQL 5.6 及更早版本中使用 InnoDB 表时,索引键前缀限制为 767 字节。具有 255 个字符长度和 utf8mb4 编码的字符串列超过了该限制。这意味着任何类型为 string 且 unique=true 的列都必须将其最大 length 设置为 190。否则,您将看到此错误:"[PDOException] SQLSTATE[42000]: Syntax error or access violation: 1071 Specified key was too long; max key length is 767 bytes"。
此类称为“实体”。很快,您就可以将 Product 对象保存到数据库中的 product 表并进行查询。 Product 实体中的每个属性都可以映射到该表中的一列。这通常使用属性来完成:您在每个属性上方看到的 #[ORM\Column(...)] 注释。
make:entity 命令是一个使生活更轻松的工具。但这是您的代码:添加/删除字段,添加/删除方法或更新配置。
Doctrine 支持各种各样的字段类型,每种类型都有自己的选项。请查看 Doctrine 文档中的 Doctrine 映射类型列表。如果您想使用 XML 而不是属性,请在您的 config/packages/doctrine.yaml 文件中的实体映射中添加 type: xml 和 dir: '%kernel.project_dir%/config/doctrine'。
警告
注意不要使用保留的 SQL 关键字作为表名或列名(例如 GROUP 或 USER)。有关如何转义这些关键字的详细信息,请参阅 Doctrine 的 保留 SQL 关键字文档。或者,使用类上方的 #[ORM\Table(name: 'groups')] 更改表名,或使用 name: 'group_name' 选项配置列名。
迁移:创建数据库表/Schema
Product 类已完全配置,可以保存到 product 表中。如果您刚刚定义了这个类,您的数据库实际上还没有 product 表。要添加它,您可以利用已经安装的 DoctrineMigrationsBundle:
1
$ php bin/console make:migration提示
从 MakerBundle: v1.56.0 开始 - 将 --formatted 传递给 make:migration 会生成一个美观整洁的迁移文件。
如果一切正常,您应该看到类似这样的内容:
1 2 3 4
SUCCESS!
Next: Review the new migration "migrations/Version20211116204726.php"
Then: Run the migration with php bin/console doctrine:migrations:migrate如果您打开此文件,它包含更新数据库所需的 SQL!要运行该 SQL,请执行您的迁移:
1
$ php bin/console doctrine:migrations:migrate此命令执行所有尚未针对您的数据库运行的迁移文件。当您部署到生产环境时,您应该运行此命令以保持您的生产数据库最新。
迁移 & 添加更多字段
但是,如果您需要向 Product 添加新的字段属性,例如 description,该怎么办?您可以编辑该类以添加新的属性。但是,您也可以再次使用 make:entity:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
$ php bin/console make:entity
Class name of the entity to create or update
> Product
New property name (press <return> to stop adding fields):
> description
Field type (enter ? to see all types) [string]:
> text
Can this field be null in the database (nullable) (yes/no) [no]:
> no
New property name (press <return> to stop adding fields):
>
(press enter again to finish)这将添加新的 description 属性以及 getDescription() 和 setDescription() 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
// src/Entity/Product.php
// ...
+ use Doctrine\DBAL\Types\Types;
class Product
{
// ...
+ #[ORM\Column(type: Types::TEXT)]
+ private string $description;
// getDescription() & setDescription() were also added
}新属性已映射,但它在 product 表中尚不存在。没问题!生成新的迁移:
1
$ php bin/console make:migration这次,生成的文件中的 SQL 将如下所示:
1
ALTER TABLE product ADD description LONGTEXT NOT NULL迁移系统是智能的。它将您的所有实体与数据库的当前状态进行比较,并生成同步它们所需的 SQL!像以前一样,执行您的迁移:
1
$ php bin/console doctrine:migrations:migrate警告
如果您使用的是 SQLite 数据库,您将看到以下错误:PDOException: SQLSTATE[HY000]: General error: 1 Cannot add a NOT NULL column with default value NULL。将 nullable=true 选项添加到 description 属性以解决该问题。
这将仅执行一个新的迁移文件,因为 DoctrineMigrationsBundle 知道第一个迁移已在较早之前执行。在后台,它管理一个 migration_versions 表来跟踪此信息。
每次您更改 schema 时,运行这两个命令以生成迁移,然后执行它。请务必提交迁移文件并在部署时执行它们。
提示
如果您更喜欢手动添加新属性,make:entity 命令可以为您生成 getter 和 setter 方法:
1
$ php bin/console make:entity --regenerate如果您进行了一些更改并希望重新生成所有 getter/setter 方法,也请传递 --overwrite。
将对象持久化到数据库
现在是将 Product 对象保存到数据库的时候了!让我们创建一个新的控制器来进行实验:
1
$ php bin/console make:controller ProductController在控制器内部,您可以创建一个新的 Product 对象,在其上设置数据,然后保存它:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
// ...
use App\Entity\Product;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManagerInterface;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product', name: 'create_product')]
public function createProduct(EntityManagerInterface $entityManager): Response
{
$product = new Product();
$product->setName('Keyboard');
$product->setPrice(1999);
$product->setDescription('Ergonomic and stylish!');
// tell Doctrine you want to (eventually) save the Product (no queries yet)
$entityManager->persist($product);
// actually executes the queries (i.e. the INSERT query)
$entityManager->flush();
return new Response('Saved new product with id '.$product->getId());
}
}试一下!
恭喜!您刚刚在 product 表中创建了您的第一行。为了证明这一点,您可以直接查询数据库:
1 2 3 4
$ php bin/console dbal:run-sql 'SELECT * FROM product'
# on Windows systems not using Powershell, run this command instead:
# php bin/console dbal:run-sql "SELECT * FROM product"更详细地查看前面的示例:
- 第 13 行
EntityManagerInterface $entityManager参数告诉 Symfony 将 实体管理器服务注入到控制器方法中。此对象负责将对象保存到数据库以及从数据库获取对象。 - 第 15-18 行 在本节中,您像处理任何其他普通 PHP 对象一样实例化和处理
$product对象。 - 第 21 行
persist($product)调用告诉 Doctrine “管理”$product对象。这不会导致对数据库进行查询。 - 第 24 行 当调用
flush()方法时,Doctrine 会检查它正在管理的所有对象,以查看它们是否需要持久化到数据库。在此示例中,$product对象的数据在数据库中不存在,因此实体管理器执行INSERT查询,在product表中创建新行。
注意
如果 flush() 调用失败,则会抛出 Doctrine\ORM\ORMException 异常。请参阅 事务和并发。
无论您是创建还是更新对象,工作流程始终相同:Doctrine 足够智能,可以知道它应该 INSERT 还是 UPDATE 您的实体。
验证对象
Symfony 验证器可以重用 Doctrine 元数据来执行一些基本的验证任务。首先,添加或配置 auto_mapping 选项,以定义哪些实体应由 Symfony 自省以添加自动验证约束。
考虑以下控制器代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Validator\ValidatorInterface;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product', name: 'create_product')]
public function createProduct(ValidatorInterface $validator): Response
{
$product = new Product();
// ... update the product data somehow (e.g. with a form) ...
$errors = $validator->validate($product);
if (count($errors) > 0) {
return new Response((string) $errors, 400);
}
// ...
}
}尽管 Product 实体未定义任何显式的 验证配置,但如果 auto_mapping 选项将其包含在要自省的实体列表中,则 Symfony 将为其推断一些验证规则并将应用它们。
例如,考虑到 name 属性在数据库中不能为 null,则会自动向该属性添加 NotNull 约束(如果它尚未包含该约束)。
下表总结了 Doctrine 元数据与 Symfony 自动添加的相应验证约束之间的映射:
| Doctrine 属性 | 验证约束 | 注释 |
|---|---|---|
nullable=false |
NotNull | 需要安装 PropertyInfo 组件 |
type |
Type | 需要安装 PropertyInfo 组件 |
unique=true |
UniqueEntity | |
length |
Length |
由于 Form 组件以及 API Platform 在内部都使用 Validator 组件,因此您的所有表单和 Web API 也将自动受益于这些自动验证约束。
这种自动验证是提高生产力的一个不错的功能,但它不能完全取代验证配置。您仍然需要添加一些 验证约束,以确保用户提供的数据是正确的。
从数据库获取对象
从数据库中取回对象甚至更容易。假设您希望能够访问 /product/1 来查看您的新产品:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManagerInterface;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product/{id}', name: 'product_show')]
public function show(EntityManagerInterface $entityManager, int $id): Response
{
$product = $entityManager->getRepository(Product::class)->find($id);
if (!$product) {
throw $this->createNotFoundException(
'No product found for id '.$id
);
}
return new Response('Check out this great product: '.$product->getName());
// or render a template
// in the template, print things with {{ product.name }}
// return $this->render('product/show.html.twig', ['product' => $product]);
}
}另一种可能性是使用 ProductRepository,通过 Symfony 的自动装配并由依赖注入容器注入:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use App\Repository\ProductRepository;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product/{id}', name: 'product_show')]
public function show(ProductRepository $productRepository, int $id): Response
{
$product = $productRepository
->find($id);
// ...
}
}试一下!
当您查询特定类型的对象时,您始终使用所谓的“仓库”(repository)。您可以将仓库视为一个 PHP 类,其唯一的工作是帮助您获取特定类的实体。
一旦您拥有了仓库对象,您就拥有了许多辅助方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
$repository = $entityManager->getRepository(Product::class);
// look for a single Product by its primary key (usually "id")
$product = $repository->find($id);
// look for a single Product by name
$product = $repository->findOneBy(['name' => 'Keyboard']);
// or find by name and price
$product = $repository->findOneBy([
'name' => 'Keyboard',
'price' => 1999,
]);
// look for multiple Product objects matching the name, ordered by price
$products = $repository->findBy(
['name' => 'Keyboard'],
['price' => 'ASC']
);
// look for *all* Product objects
$products = $repository->findAll();您还可以添加自定义方法以进行更复杂的查询!更多信息请参见数据库和 Doctrine ORM 部分。
提示
当渲染 HTML 页面时,页面底部的 Web 调试工具栏将显示查询的数量以及执行它们所花费的时间
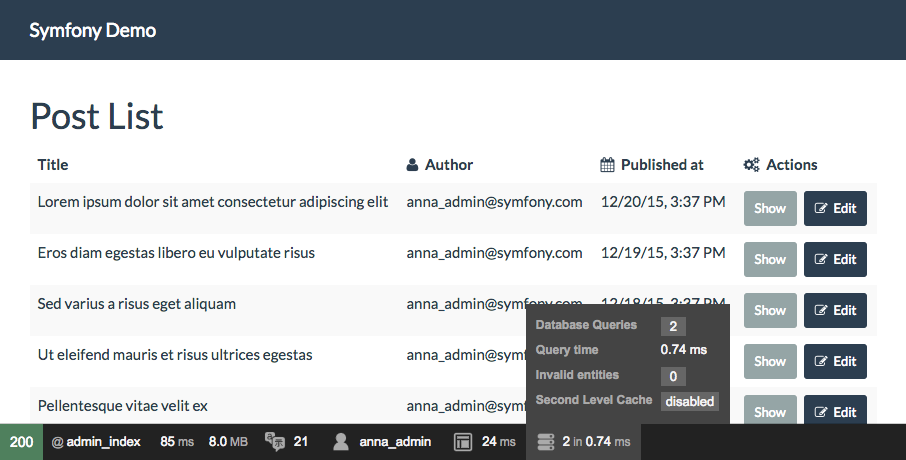
如果数据库查询数量过多,图标将变为黄色,以指示某些内容可能不正确。单击图标以打开 Symfony 分析器,并查看已执行的确切查询。如果您没有看到 Web 调试工具栏,请安装 profiler Symfony pack,方法是运行以下命令:composer require --dev symfony/profiler-pack。
有关更多信息,请阅读 Symfony 分析器文档。
自动获取对象 (EntityValueResolver)
2.7.1
EntityValueResolver 的自动装配在 DoctrineBundle 2.7.1 中引入。
在许多情况下,您可以使用 EntityValueResolver 为您自动执行查询!您可以将控制器简化为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use App\Repository\ProductRepository;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product/{id}')]
public function show(Product $product): Response
{
// use the Product!
// ...
}
}就是这样!该 bundle 使用路由中的 {id} 来查询 Product,通过 id 列。如果未找到,则会生成 404 页面。
提示
全局启用后,可以通过使用设置为 disabled 的 MapEntity 在特定控制器上禁用此行为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
public function show(
#[CurrentUser]
#[MapEntity(disabled: true)]
User $user
): Response {
// User is not resolved by the EntityValueResolver
// ...
}自动获取
如果您的路由通配符与实体上的属性匹配,则解析器将自动获取它们
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
/**
* Fetch via primary key because {id} is in the route.
*/
#[Route('/product/{id}')]
public function showByPk(Product $product): Response
{
}
/**
* Perform a findOneBy() where the slug property matches {slug}.
*/
#[Route('/product/{slug}')]
public function showBySlug(Product $product): Response
{
}自动获取在以下情况下有效
- 如果
{id}在您的路由中,则它用于通过find()方法按主键获取。 - 解析器将尝试通过使用路由中所有实际上是实体属性的通配符(非属性将被忽略)来执行
findOneBy()获取。
此行为默认在所有控制器上启用。如果您愿意,您可以将此功能限制为仅在名为 id 的路由通配符上工作,以按主键查找实体。为此,请将选项 doctrine.orm.controller_resolver.auto_mapping 设置为 false。
当 auto_mapping 被禁用时,您可以使用 MapEntity 属性为任何控制器参数显式配置映射。您甚至可以使用 MapEntity 选项来控制 EntityValueResolver 的行为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use Symfony\Bridge\Doctrine\Attribute\MapEntity;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product/{slug}')]
public function show(
#[MapEntity(mapping: ['slug' => 'slug'])]
Product $product
): Response {
// use the Product!
// ...
}
}通过表达式获取
如果自动获取不适用于您的用例,您可以使用 ExpressionLanguage 组件编写表达式
1 2 3 4 5 6
#[Route('/product/{product_id}')]
public function show(
#[MapEntity(expr: 'repository.find(product_id)')]
Product $product
): Response {
}在表达式中,repository 变量将是您实体的 Repository 类,任何路由通配符(如 {product_id})都可用作变量。
表达式中调用的仓库方法也可以返回实体列表。在这种情况下,请更新控制器参数的类型
1 2 3 4 5 6
#[Route('/posts_by/{author_id}')]
public function authorPosts(
#[MapEntity(class: Post::class, expr: 'repository.findBy({"author": author_id}, {}, 10)')]
iterable $posts
): Response {
}7.1
实体列表的映射在 Symfony 7.1 中引入。
这也可以用于帮助解析多个参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
#[Route('/product/{id}/comments/{comment_id}')]
public function show(
Product $product,
#[MapEntity(expr: 'repository.find(comment_id)')]
Comment $comment
): Response {
}在上面的示例中,$product 参数是自动处理的,但 $comment 是使用属性配置的,因为它们不能都遵循默认约定。
如果您需要从请求中获取其他信息来查询数据库,您还可以通过 request 变量在表达式中访问请求。假设您想要根据名为 sort 的查询参数获取产品的第一个或最后一个评论
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
#[Route('/product/{id}/comments')]
public function show(
Product $product,
#[MapEntity(expr: 'repository.findOneBy({"product": id}, {"createdAt": request.query.get("sort", "DESC")})')]
Comment $comment
): Response {
}MapEntity 选项
MapEntity 属性上有许多选项可用于控制行为
id-
如果配置了
id选项并且与路由参数匹配,则解析器将按主键查找1 2 3 4 5 6
#[Route('/product/{product_id}')] public function show( #[MapEntity(id: 'product_id')] Product $product ): Response { } mapping-
配置与
findOneBy()方法一起使用的属性和值:键是路由占位符名称,值是 Doctrine 属性名称1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
#[Route('/product/{category}/{slug}/comments/{comment_slug}')] public function show( #[MapEntity(mapping: ['category' => 'category', 'slug' => 'slug'])] Product $product, #[MapEntity(mapping: ['comment_slug' => 'slug'])] Comment $comment ): Response { } exclude-
配置应在
findOneBy()方法中使用的属性,方法是排除一个或多个属性,以便不使用所有属性1 2 3 4 5 6 7
#[Route('/product/{slug}/{date}')] public function show( #[MapEntity(exclude: ['date'])] Product $product, \DateTime $date ): Response { } stripNull- 如果为 true,则当使用
findOneBy()时,任何为null的值将不会用于查询。 objectManager-
默认情况下,
EntityValueResolver使用默认对象管理器,但您可以配置它1 2 3 4 5 6
#[Route('/product/{id}')] public function show( #[MapEntity(objectManager: 'foo')] Product $product ): Response { } evictCache- 如果为 true,则强制 Doctrine 始终从数据库而不是缓存中获取实体。
disabled- 如果为 true,则
EntityValueResolver将不会尝试替换参数。 message-
当出现 NotFoundHttpException 时显示的(可选)自定义消息,但仅在开发环境中(您不会在生产环境中看到此消息)
1 2 3 4 5 6
#[Route('/product/{product_id}')] public function show( #[MapEntity(id: 'product_id', message: 'The product does not exist')] Product $product ): Response { }
7.1
message 选项在 Symfony 7.1 中引入。
更新对象
一旦您从 Doctrine 获取了一个对象,您就可以像使用任何 PHP 模型一样与它交互
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use App\Repository\ProductRepository;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManagerInterface;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product/edit/{id}', name: 'product_edit')]
public function update(EntityManagerInterface $entityManager, int $id): Response
{
$product = $entityManager->getRepository(Product::class)->find($id);
if (!$product) {
throw $this->createNotFoundException(
'No product found for id '.$id
);
}
$product->setName('New product name!');
$entityManager->flush();
return $this->redirectToRoute('product_show', [
'id' => $product->getId()
]);
}
}使用 Doctrine 编辑现有产品包括三个步骤
- 从 Doctrine 获取对象;
- 修改对象;
- 在实体管理器上调用
flush()。
您可以调用 $entityManager->persist($product),但这没有必要:Doctrine 已经在“监视”您的对象以进行更改。
删除对象
删除对象非常相似,但需要调用实体管理器的 remove() 方法
1 2
$entityManager->remove($product);
$entityManager->flush();正如您可能期望的那样,remove() 方法通知 Doctrine 您想要从数据库中删除给定的对象。DELETE 查询实际上在调用 flush() 方法之前不会执行。
查询对象:Repository
您已经看到了仓库对象如何让您无需任何工作即可运行基本查询
1 2 3
// from inside a controller
$repository = $entityManager->getRepository(Product::class);
$product = $repository->find($id);但是,如果您需要更复杂的查询怎么办?当您使用 make:entity 生成实体时,该命令还生成了一个 ProductRepository 类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
// src/Repository/ProductRepository.php
namespace App\Repository;
use App\Entity\Product;
use Doctrine\Bundle\DoctrineBundle\Repository\ServiceEntityRepository;
use Doctrine\Persistence\ManagerRegistry;
class ProductRepository extends ServiceEntityRepository
{
public function __construct(ManagerRegistry $registry)
{
parent::__construct($registry, Product::class);
}
}当您获取仓库时(即 ->getRepository(Product::class)),它实际上是此对象的实例!这是因为在您的 Product 实体类的顶部生成的 repositoryClass 配置。
假设您要查询价格高于某个价格的所有 Product 对象。为此,请向您的仓库添加一个新方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
// src/Repository/ProductRepository.php
// ...
class ProductRepository extends ServiceEntityRepository
{
public function __construct(ManagerRegistry $registry)
{
parent::__construct($registry, Product::class);
}
/**
* @return Product[]
*/
public function findAllGreaterThanPrice(int $price): array
{
$entityManager = $this->getEntityManager();
$query = $entityManager->createQuery(
'SELECT p
FROM App\Entity\Product p
WHERE p.price > :price
ORDER BY p.price ASC'
)->setParameter('price', $price);
// returns an array of Product objects
return $query->getResult();
}
}传递给 createQuery() 的字符串可能看起来像 SQL,但它是 Doctrine Query Language。这允许您使用常用的查询语言键入查询,但引用 PHP 对象(即在 FROM 语句中)。
现在,您可以在仓库上调用此方法
1 2 3 4 5 6
// from inside a controller
$minPrice = 1000;
$products = $entityManager->getRepository(Product::class)->findAllGreaterThanPrice($minPrice);
// ...有关如何将仓库注入到任何服务中,请参阅 服务容器。
使用 Query Builder 查询
Doctrine 还提供了一个 Query Builder,这是一种面向对象的方式来编写查询。当查询是动态构建的(即基于 PHP 条件)时,建议使用它
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
// src/Repository/ProductRepository.php
// ...
class ProductRepository extends ServiceEntityRepository
{
public function findAllGreaterThanPrice(int $price, bool $includeUnavailableProducts = false): array
{
// automatically knows to select Products
// the "p" is an alias you'll use in the rest of the query
$qb = $this->createQueryBuilder('p')
->where('p.price > :price')
->setParameter('price', $price)
->orderBy('p.price', 'ASC');
if (!$includeUnavailableProducts) {
$qb->andWhere('p.available = TRUE');
}
$query = $qb->getQuery();
return $query->execute();
// to get just one result:
// $product = $query->setMaxResults(1)->getOneOrNullResult();
}
}使用 SQL 查询
此外,如果需要,您可以直接使用 SQL 查询
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
// src/Repository/ProductRepository.php
// ...
class ProductRepository extends ServiceEntityRepository
{
public function findAllGreaterThanPrice(int $price): array
{
$conn = $this->getEntityManager()->getConnection();
$sql = '
SELECT * FROM product p
WHERE p.price > :price
ORDER BY p.price ASC
';
$resultSet = $conn->executeQuery($sql, ['price' => $price]);
// returns an array of arrays (i.e. a raw data set)
return $resultSet->fetchAllAssociative();
}
}使用 SQL,您将获得原始数据,而不是对象(除非您使用 NativeQuery 功能)。
配置
请参阅 Doctrine 配置参考。
关系和关联
Doctrine 提供了管理数据库关系(也称为关联)所需的所有功能,包括 ManyToOne、OneToMany、OneToOne 和 ManyToMany 关系。
有关信息,请参阅 如何使用 Doctrine 关联/关系。
数据库测试
阅读关于 测试与数据库交互的代码的文章。
Doctrine 扩展 (Timestampable, Translatable 等)
Doctrine 社区创建了一些扩展来满足常见需求,例如“在创建实体时自动设置 createdAt 属性的值”。阅读有关 可用的 Doctrine 扩展的更多信息,并使用 StofDoctrineExtensionsBundle 将它们集成到您的应用程序中。